What is Blood Pressure?
Blood is carried from the heart to all parts of your body in vessels called arteries.
Blood pressure measures how hard your heart is working to keep you alive and specifically, it is the force of the blood pushing against the walls of the arteries. Each time the heart beats (about 60-70 times a minute at rest), it pumps out blood into the arteries. When your heart beats and pumps your blood, your blood pressure rises which is called systolic pressure. When the heart is at rest, between beats, your blood pressure falls and this is referred to as diastolic pressure.
Blood pressure changes during the day. It is lowest as you sleep and rises when you get up. It also can rise when you are excited, nervous, or exercise.
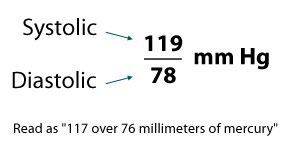
Systolic
The top number, which is also the higher of the two numbers, measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats (when the heart muscle contracts).
Diastolic
The bottom number, which is also the lower of the two numbers, measures the pressure in the arteries between heartbeats (when the heart muscle is resting between beats and refilling with blood).
So what does the American Heart Association (AHA) recommend for healthy blood pressure?
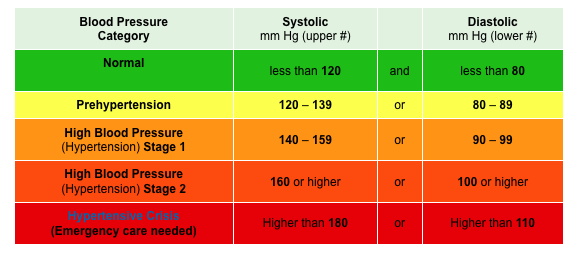
For most of your waking hours, your blood pressure stays pretty much the same when you are sitting or standing still. That level should be lower than 120/80. When the level stays high, 140/90 or higher, you have high blood pressure. With high blood pressure, the heart works harder, your arteries take a beating, and your chances of a stroke, heart attack, and kidney problems are greater.
Why Track Blood Pressure?
As we age, the risk for high blood pressure (hypertension) rises. High blood pressure can lead to cardio vascular disease, strokes, and other health issues. However, regular physical activity (exercise) makes your heart stronger.
A stronger heart can pump more blood with less effort. If your heart can work less to pump, the force on your arteries decreases, lowering your blood pressure. Whether you currently have high blood pressure or looking to maintain healthy blood pressure, exercise is a highly effective tool for a healthy heart and Fitdigits can track it all on your iPhone or Android.
In fact, studies show that regular exercise can reduce your systolic blood pressure by an average of 5 to 10 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). For some people, exercise is enough to reduce the need for blood pressure medication or eliminate the need altogether.
If your blood pressure is at a desirable level — less than 120/80 mm Hg — exercise can keep it from rising as you age. Regular exercise also helps you maintain a healthy weight, another important way to control blood pressure.
Can I exercise to lower my blood pressure?
Adding a moderate amount of exercise for 20-30 minutes per day is enough to experience the benefits. For example, jog, play tennis, try hiking or use the elliptical machine at the gym. Then, add a brisk walk a few days a week, too. The idea is to increase your heart rate during exercise and track it using Fitdigits and a heart rate monitor belt. Use heart rate zones to guide your effort level and try to get your heart rate in Zones 2 and 3 for at least some of your exercise.
For your overall activity, try to increase the amount of steps throughout the day. For example, park at the end of the parking lot, take the stairs and walk around the block while you talk on the phone rather than sit in your desk. Try to achieve 10,000 steps per day and track this using Fitbit which will automatically sync to your Fitdigits account.
Since it takes about one to three months for regular exercise to affect your blood pressure, it’s important to continue exercising. If you want long-term health benefits, consider these changes as lifestyle improvements.
Sources: American Heart Association, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Life Clinic, Mayo Clinic, Livestrong and Wikipedia.
This article was great in suggesting new brands and
styles to try out.
, I thought this article was suppose
to help those of us who have never used Blood Pressure Monitor
Thank you so much for this comprehensive list!
I have read many reviews and done a ton of research
. This has helped me make decisions on Blood Pressure Monitor.
.I am completely happy with your website
. All comments and articles
are very useful and very good. Your blog is very
careful-take control.
I am loving all of the inside ,
<a href="http://www.easyfit.in" title="Blood Pressure Monitor"
target="_blank">Blood Pressure Monitor</a>